What are Monoclonal Antibodies?
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) are a class of antibodies that are derived from a single, cloned immune cell. Unlike polyclonal antibodies (derived from a mixture of different immune cells), mAbs originate from a single B-cell clone, ensuring uniformity in their specificity and action. This unique attribute renders them highly effective in targeting specific antigens with precision. This article on Application of Monoclonal Antibodies, we will study the diverse uses of mAbs in disease treatment and research.
Learn more: Hybridoma Technology Short Notes
Application of Monoclonal Antibodies
The versatile applications of monoclonal antibodies, as we said earlier, is in medicine and research, are summarized below:
Learn more: MCQ on Monoclonal Antibodies
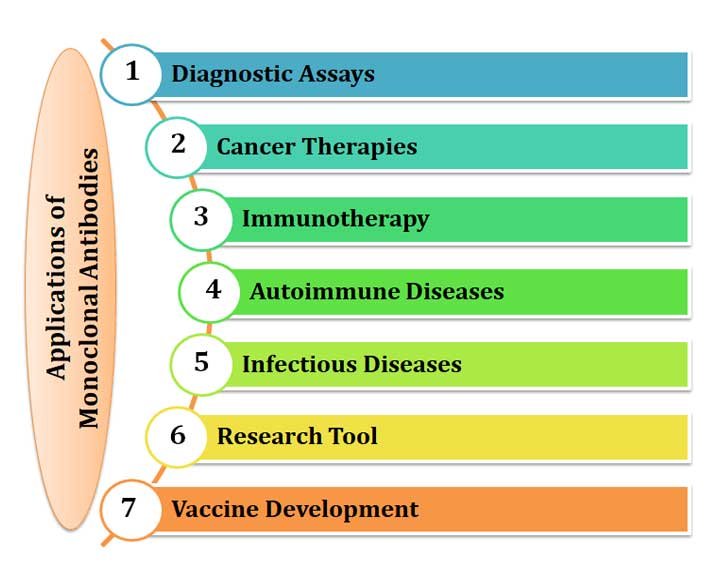
(1). Diagnostic Assays
Ø Monoclonal antibodies serve as critical components in diagnostic tools like Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays (ELISA).
Ø ELISA enable the rapid and accurate detection of many diseases, including infectious agents, cancer biomarkers, and autoimmune disorders.
Ø The specificity of monoclonal antibodies ensures reliable and sensitive results
Ø This facilitates early disease detection and effective patient management
You may like our: Biotechnology Notes | Biotechnology PPT | Biotechnology MCQ |
(2). Cancer Therapies
Ø Monoclonal antibodies have revolutionized cancer treatment through targeted therapies.
Ø Example: Trastuzumab (Herceptin) for HER2-positive breast cancer and Rituximab (Rituxan) for B-cell lymphomas.
Ø These antibodies bind to specific cancer cells, inhibiting their growth or marking them for destruction by the immune system.
Ø Monoclonal antibodies also facilitate drug delivery by conjugating chemotherapy agents, enhancing their specificity and reducing adverse effects.
(3). Immunotherapy
Ø Monoclonal antibodies play a pivotal role in immunotherapy, which harnesses the body’s immune system to combat diseases.
Ø Example: Immune checkpoint inhibitors like Pembrolizumab and Nivolumab block molecules that inhibit immune responses, enabling immune cells to attack cancer cells more effectively.
Ø Additionally, chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies utilize monoclonal antibodies to engineer patients’ immune cells for targeted cancer cell recognition.
(4). Autoimmune Diseases
Ø Monoclonal antibodies have revolutionized the treatment of autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and inflammatory diseases.
Ø By targeting specific molecules involved in immune responses, these antibodies modulate aberrant immune reactions, reducing inflammation and disease progression.
(5). Infectious Diseases
Ø Monoclonal antibodies can neutralize viruses by binding to specific viral proteins and thus can prevent their entry into host cells.
Ø They have gained prominence as potential treatments for infectious diseases by viral infections like COVID-19.
Ø Monoclonal antibodies have demonstrated therapeutic efficacy in reducing viral load and improving patient outcomes.
(6). Research Tools
Ø Monoclonal antibodies are invaluable tools in biological research.
Ø They enable the precise identification and characterization of specific molecules.
Ø They facilitate the study of protein interactions, cell signalling pathways, and gene expression, contributing to advancements in fields like cell biology, genetics, and molecular biology.
(7). Vaccine Development:
Ø mAbs play a pivotal role in vaccine research and development.
Ø They aid in identifying potential vaccine candidates, characterizing antigens, and assessing vaccine efficacy.
Ø Monoclonal antibodies have been instrumental in understanding vaccine-induced immune responses and guiding vaccine design.
Summary
Monoclonal antibodies stand as a testament to the ingenuity of scientific discovery and innovation. Their high specificity, versatility, and therapeutic potential have paved the way for transformative advancements in medicine and research. From precise diagnostics to targeted therapies and immunomodulation, monoclonal antibodies have revolutionized disease management and patient outcomes.
<<< Back to BIOTECHNOLOGY Notes
| You may also like NOTES in... | ||
|---|---|---|
| BOTANY | BIOCHEMISTRY | MOL. BIOLOGY |
| ZOOLOGY | MICROBIOLOGY | BIOSTATISTICS |
| ECOLOGY | IMMUNOLOGY | BIOTECHNOLOGY |
| GENETICS | EMBRYOLOGY | PHYSIOLOGY |
| EVOLUTION | BIOPHYSICS | BIOINFORMATICS |
| You may also like... | ||
|---|---|---|
| NOTES | QUESTION BANK | COMPETITIVE EXAMS. |
| PPTs | UNIVERSITY EXAMS | DIFFERENCE BETWEEN.. |
| MCQs | PLUS ONE BIOLOGY | NEWS & JOBS |
| MOCK TESTS | PLUS TWO BIOLOGY | PRACTICAL |
