“Science is a way of thinking much more than it is a body of knowledge…”
Carl Sagan
Learning objectives: What is scientific methodology? | Steps of Scientific Method | Hypothesis Concept | What is an Experiment? | What is ‘Testing of Hypothesis’? | What is Theory? | Inductive vs Deductive reasoning
What is Scientific Methodology?
Ø. Also called the Scientific Method.
Ø. The scientific method is an empirical (=Experimental) method of acquiring knowledge.
Ø. It is a set of methods of enquiry in Science. All methods cannot be scientific.
Ø. To be termed scientific, the method of inquiry must be based on:
$. Gathering observable, empirical (experimental) and measurable evidence subjected to specific principles of reasoning.
Ø. The scientific method is the logical scheme used by scientists searching for the answers to a question posed within the science.
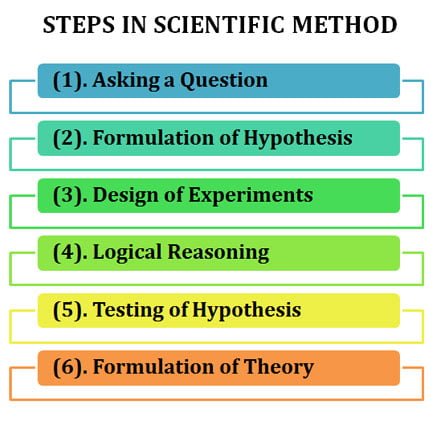
Steps if Scientific Method
Ø. The Scientific Method includes the following SIX steps:
(1). Asking a question / observation and thoughts
(2). Formulation of hypothesis
(3). Design of experiments
(4). Deduction (Logical Reasoning)
(5). Testing of hypothesis
(6). Formulation of theory
(1). Asking a Question
Ø. The first step in the scientific method.
Ø. The question should be in the contest of existing knowledge or theory or observation or thoughts.
Ø. The question in the scientific method may be of TWO types
(1). A new question that old theories are not capable of answering.
(2). A new question that call for the formulation of a new theory.
(2). Formulation of hypothesis
Ø The second step in scientific method.
Ø Hypothesis Definition: “a supposition (belief) or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation”.
Ø Hypothesis is developed as the tentative answer to the question.
Ø Hypothesis is a possible explanation of some phenomena we observed.
Things to remember when constructing a hypothesis:
$. Hypothesis must be logically consistent; one cannot test a hypothesis that contradicts itself.
$. Should be consistent with most of the available knowledge on the subject.
$. Hypothesis should offer an explanation of the phenomenon under the investigation.
$. It must suggest consequences that are empirically (experimentally) testable
$. Hypothesis should make a prediction that can be checked against reality.
(3). Design of Experiments
Learn more: Principles of Design of Experiments
Learn more: Type of Experimental Designs in Statistics
Ø Experiment Definition: “An experiment is a methodical procedure carried out with the goal of verifying, falsifying or establishing the accuracy of a hypothesis”.
Ø It is the main turning point in the development of science.
Ø It is also used for testing the existing theory or new hypothesis in order to support them or disprove them.
Ø The experiment gives results (data).
Learn More: Data / Variables in Statistics (Biostatistics Lecture Notes)
Ø All data should be collected in a constant manner so that meaningful comparison can be made with statistical tools.
Ø One of the first decisions to be made in experimental design is the identification of parameters that have to be observed for explaining the hypothesis.
(4). Deduction (Logical Reasoning)
Ø Logical Reasoning is associated with thinking, cognition, and intellect of an individual.
Ø ‘Deduction and ‘Induction’ are two major methods in logical reasoning in Scientific Method.
Aristotle (Wikipedia)
(a). Deductive Reasoning
Ø Also called Deduction.
Ø The Deduction concept was proposed by Aristotle in the 4th century BC.
Ø Deduction Definition: “The process of reasoning from one or more statements (premises) to reach a logically certain conclusion”.
Ø Deductive reasoning links premises (evidence) with conclusions.
Ø Example:
$. All Chinese people likes rice (major premise or major evidence)
$. Mr. Lee is a Chinese (sub premise)
Deductive Reasoning: Therefore, Mr. Lee likes rice
(Source: Wikipedia)
(b). Inductive Reasoning (induction)
Ø Also called Induction.
Ø Inductive reasoning was first proposed by Francis Bacon (father of empiricism)
Learn more: Concept of Science
Ø Induction Definition: “Reasoning in which the premises (evidence) are viewed as supplying strong evidence for the truth of the conclusion”.
Ø It is a method of reasoning that derives general principles from specific observations.
Ø Example:
$. Crow is a bird that can fly. (Evidence 1)
$. Dove is a bird that can fly. (Evidence 2)
$. Parrot is a bird that can fly. (Evidence 3)
$. Sparrow is a bird that can fly. (Evidence 4)
Inductive Reasoning: “Therefore all birds can fly”
(5). Testing of hypothesis
Learn more: Testing of Hypothesis- Biostatistics Lecture Notes
Ø The true value of the hypothesis can be determined only after it has been tested.
Ø Testing of hypothesis is done after the experimentation.
Ø Experiments produce results (data).
Ø The data are first analyzed for logical reasoning (using statistical tools).
Ø Analyzed data are then tested with the test of hypothesis.
Ø Eg. t-test, f-Test, Chi-square test, ANOVA etc.
Ø Test statistics decide the possible acceptance or rejection of the hypothesis.
(5). Formulation of theory
Ø Formulation of Theory is the last step in the scientific method.
Ø Theory Definition: “A well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural phenomenon that is acquired through the scientific method and repeatedly tested and confirmed, preferably using a written, pre-defined, protocol of observations and experiments”
Ø A theory is a hypothesis, or a group of related hypotheses, which has been confirmed through repeated experimental tests.
Ø Scientific theories are the most reliable, rigorous, and comprehensive form of scientific knowledge.
Learn more: Science and Scientific Knowledge
Ø Theories and Laws are not exact, they have some differences.
Ø The scientific law is the description of an observed phenomenon. It doesn’t explain why the phenomenon exists or what causes it. The explanation of a phenomenon is known as a scientific theory.
Ø Theories have universal applicability and acceptability.
Ø Theories become part of our understanding of the universe.
Ø They help to explore the less understood areas of knowledge.
<<< Back to RESEARCH METHODOLOGY Page
You might also like…
@. Concept of Science and Scientific Knowledge
@. Data – Collection and Classification
@. Date Representation Methods: Part 1 | Part 2 | Part 3 |
@. Principles of Design of Experiments
@. Statistical Test of Hypothesis
More Lecture Notes from Easy Biology Class…
BotanyZoologyBiochemistryGeneticsCell & Molecular BiologyBiotechnologyPhysiology & EndocrinologyPlant PhysiologyMicrobiologyImmunologyEmbryologyEcologyEvolutionBiophysicsResearch MethodologyBiostatisticsChemistry for BiologistsPhysics for Biologists
Browse more in Easy Biology Class…
Lecture NotesBiology PPTsVideo TutorialsBiology MCQQuestion BankDifference betweenPractical AidsMock Tests (Online)Biology Exams