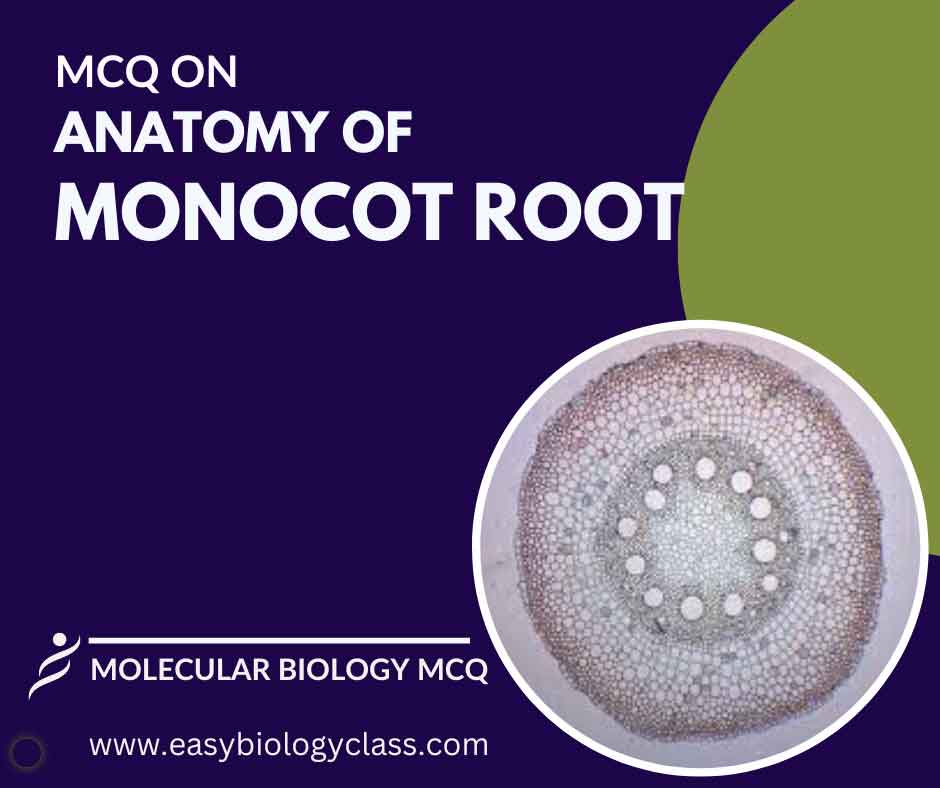
A monocot root comprises an epidermis with root hairs, a cortex for storage, and an endodermis with a Casparian strip. The vascular cylinder contains xylem and phloem arranged in a ring. Root cap protects the growing tip, aiding in soil penetration. This is an MCQ on Anatomy of Monocot Root.
Botany Notes | Botany PPTs | Botany MCQs
You may also like...
NOTES QUESTION BANK COMPETITIVE EXAMS.
PPTs UNIVERSITY EXAMS DIFFERENCE BETWEEN..
MCQs PLUS ONE BIOLOGY NEWS & JOBS
MOCK TESTS PLUS TWO BIOLOGY PRACTICAL