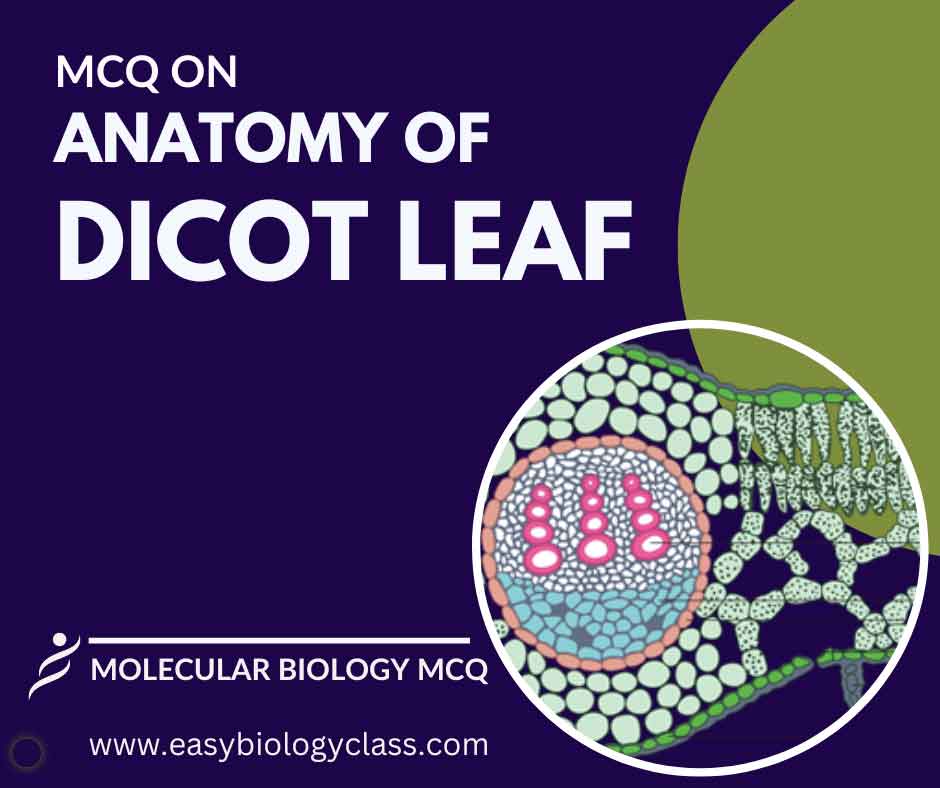
A dicot leaf typically exhibits a broad, flattened shape with a reticulate venation pattern. Its structure includes an epidermis, mesophyll with palisade and spongy layers, vascular bundles arranged in a ring, and stomata for gas exchange on the lower epidermis. This is an MCQ on Anatomy of Dicot Leaf.
Botany Notes | Botany PPTs | Botany MCQs
You may also like...
NOTES QUESTION BANK COMPETITIVE EXAMS.
PPTs UNIVERSITY EXAMS DIFFERENCE BETWEEN..
MCQs PLUS ONE BIOLOGY NEWS & JOBS
MOCK TESTS PLUS TWO BIOLOGY PRACTICAL