Cladistics is a phylogenetic classification method based on shared evolutionary traits, emphasizing common ancestry and phylogenetic relationships among organisms. Performing a cladistic analysis of a group of taxa involves a systematic process of character coding, character state identification, and the construction of a cladogram (phylogenetic tree). Here are the basic steps to the Methodology of Cladistics.
Evolution Notes | Evolution PPTs | Evolution MCQs
Methodology of Cladistics

(1). Define Your Taxa
Ø Begin by clearly defining the group of organisms (taxa) you want to analyse.
Ø This group can range from species to higher taxonomic categories like genera or families.
Ø Example: Cladistic analysis of the aquatic birds belongs to Aequornithes.
Learn more: Principles of Cladistics
(2). Select Characters and Character States
Ø Identify a set of morphological, genetic, or molecular characters that you believe will be informative for your analysis.
Ø These characters (data) should be discrete and measurable, meaning they can be categorized into different states.
Ø For example, if you are analysing bird species, characters could include beak shape, wing length, or feather colour.
Ø For molecular analyses, you might use DNA or RNA or Protein sequences.
(3). Code Characters
Ø Assign character states to each taxon in your dataset.
Ø Taxa can be coded as either possessing (1) or lacking (0) a particular character state.
Ø Alternatively, you can use a numeric coding system to represent different character states.
| You may also like NOTES in... | ||
|---|---|---|
| BOTANY | BIOCHEMISTRY | MOL. BIOLOGY |
| ZOOLOGY | MICROBIOLOGY | BIOSTATISTICS |
| ECOLOGY | IMMUNOLOGY | BIOTECHNOLOGY |
| GENETICS | EMBRYOLOGY | PHYSIOLOGY |
| EVOLUTION | BIOPHYSICS | BIOINFORMATICS |
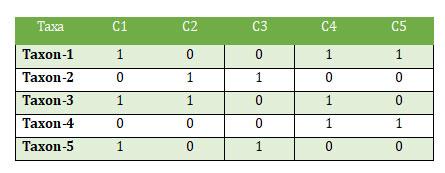
(4). Create a Character Matrix
Ø Organize your character data into a matrix.
Ø Rows represent taxa, and columns represent characters.
Ø Here is a simplified example for three taxa and five characters (C1, C2, C3, C4 and C5) of five taxa.
(5). Determine Character State Evolution
Ø Use your knowledge of biology and the characteristics of the taxa to infer which character states are ancestral (plesiomorphic) and which are derived (apomorphic).
Ø For example, if you are studying birds, feathers might be considered a derived character state as it is unique to birds among vertebrates.
(6). Root Your Tree
Ø To construct a cladogram, you will need to root it.
Ø Usually by using an outgroup taxon that is closely related to but not part of your group of interest is used.
Ø The outgroup helps identify ancestral and derived character states.
(7). Build a Data Matrix
Ø Create a data matrix where you list the characters, their character states, and their presence or absence in each taxon.
(8). Analyse the Data
Ø Use a cladistics software package or a pen-and-paper approach to analyse the data matrix.
Ø Cladistic software, like PAUP (Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony) or TNT (Tree analysis using New Technology), can conduct more complex analyses.

Ø The most common method for cladistic analysis is principle of parsimony.
Ø Principle of parsimony seeks the simplest and most likely tree by minimizing the number of character state changes (evolutionary steps) required to explain the observed data.
(9). Generate a Cladogram
Ø The software will generate a cladogram that represents the phylogenetic relationships among the taxa based on your character data.
Ø The cladogram will depict branching patterns, with nodes representing common ancestors and branches representing evolutionary relationships.
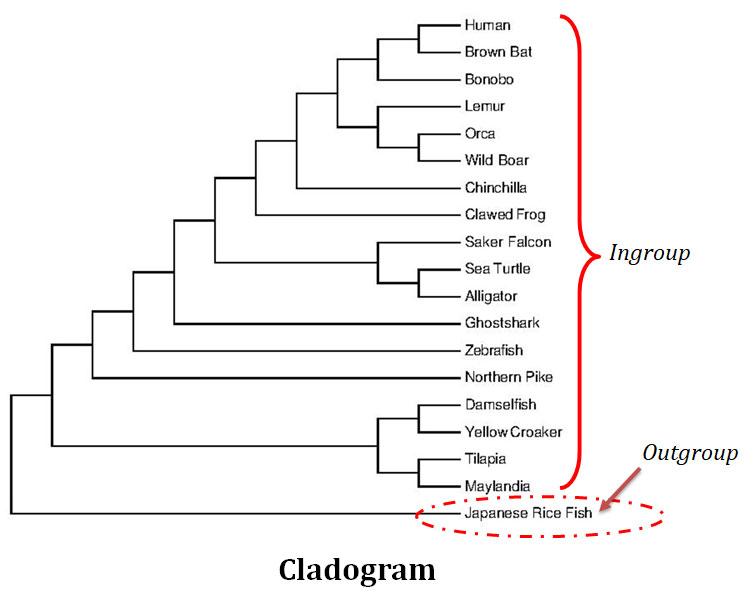
(10). Evaluate Your Cladogram
Ø Assess the support for your cladogram using measures like bootstrap values or Bremer support.
Ø Higher values indicate stronger support for specific clades.
(11). Interpret Your Results
Ø Analyse the cladogram to draw conclusions about the evolutionary relationships among your taxa.
Ø Interpret the branching patterns, noting which taxa share the most recent common ancestor and which characters define different clades.
(12). Refine and Repeat
Ø Cladistic analysis is an iterative (repetitive) process.
Ø You may need to refine your character selection or coding, rerun the analysis, and reassess your results for a better understanding.
(13). Present Your Findings
Ø Finally, communicate your cladistic analysis results through visual representations of the cladogram, tables, and explanatory text.
It is important to note that conducting a cladistic analysis can be complex and may require expertise in both the biological group that you are studying and the use of specialized software. Collaboration with experienced researchers or seeking guidance from experts in the field is often beneficial. Additionally, always consider the limitations of your data and the assumptions underlying cladistic methods.
<<< Back to Evolution Notes Page
| You may also like NOTES in... | ||
|---|---|---|
| BOTANY | BIOCHEMISTRY | MOL. BIOLOGY |
| ZOOLOGY | MICROBIOLOGY | BIOSTATISTICS |
| ECOLOGY | IMMUNOLOGY | BIOTECHNOLOGY |
| GENETICS | EMBRYOLOGY | PHYSIOLOGY |
| EVOLUTION | BIOPHYSICS | BIOINFORMATICS |
| You may also like... | ||
|---|---|---|
| NOTES | QUESTION BANK | COMPETITIVE EXAMS. |
| PPTs | UNIVERSITY EXAMS | DIFFERENCE BETWEEN.. |
| MCQs | PLUS ONE BIOLOGY | NEWS & JOBS |
| MOCK TESTS | PLUS TWO BIOLOGY | PRACTICAL |
