Kerala PSC Botany Lecturer / Assistant Professor Model Question Paper 2017 Model/Sample Question Paper of Kerala PSC Botany Lecturer/Assistant Professor Recruitment Examination to be conducted by Kerala Public Service Commission Question for the appointment of Botany Lecturer/Assistant Professor in Government Colleges of Kerala under the Directorate of Collegiate Education, Trivandrum, […]
Continue ReadingMonthly Archives: January 2017
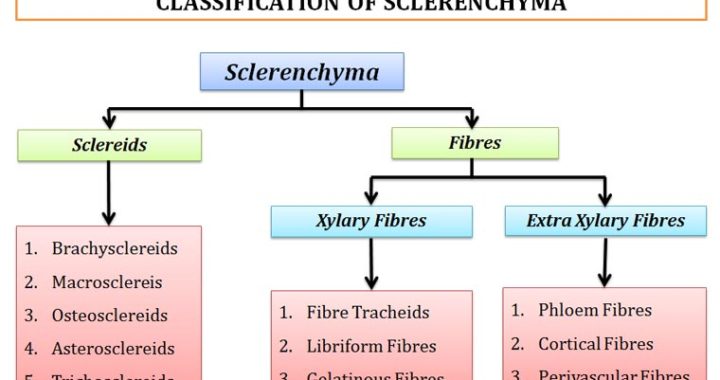
Sclerenchyma: Structure, Classification and Functions
Sclerenchyma is a simple permanent tissue in plants. Sclerenchymatous cells are dead at their maturity. Cells do not have protoplast when they completely developed. They have thick secondary cell wall. The secondary cell wall is lignified and very hard. Most of the sclerenchymatous cells show intrusive growth. The present post […]
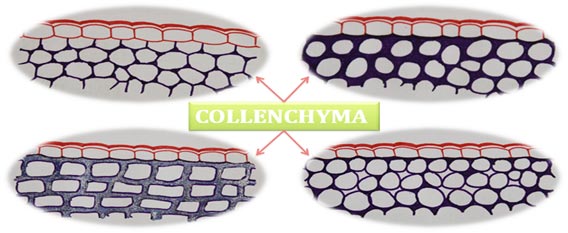
Continue ReadingCollenchyma: Structure, Classification and Functions
Collenchyma is a simple permanent tissue in plants. They are living cells with prominent nucleus and all the cell organelles. Each collenchymatous cell is with a large and prominent vacuole in the centre. The vacuole is filled with many secondary metabolites. Unlike parenchyma, the collenchyma cells possess thick primary cell […]
Continue ReadingParenchyma: Structure, Classification and Functions
The tissue (a group of cells with particular function) composed of single type of cells. Three types of simple tissue system in plants, namely (1). Parenchyma, (2). Collenchyma and (3). Sclerenchyma. The present article discusses the Structure and Types of Parenchyma Cells in Plants. Characteristics of Parenchyma (Parenchymatous Cells) Ø Parenchyma […]
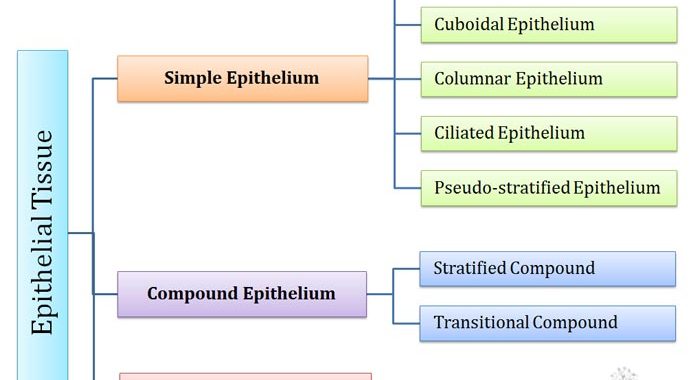
Continue ReadingEpithelial Tissue: Classification and Examples
What is Epithelium? Ø Epithelium is a tissue system in animals. Ø Epithelium constitutes the outer layer of body surfaces, linings of the alimentary canal and the walls of hollow structures. Ø It covers the internal or external surfaces of the body. Ø Epithelial cells are held together by carbohydrate […]
Continue Reading