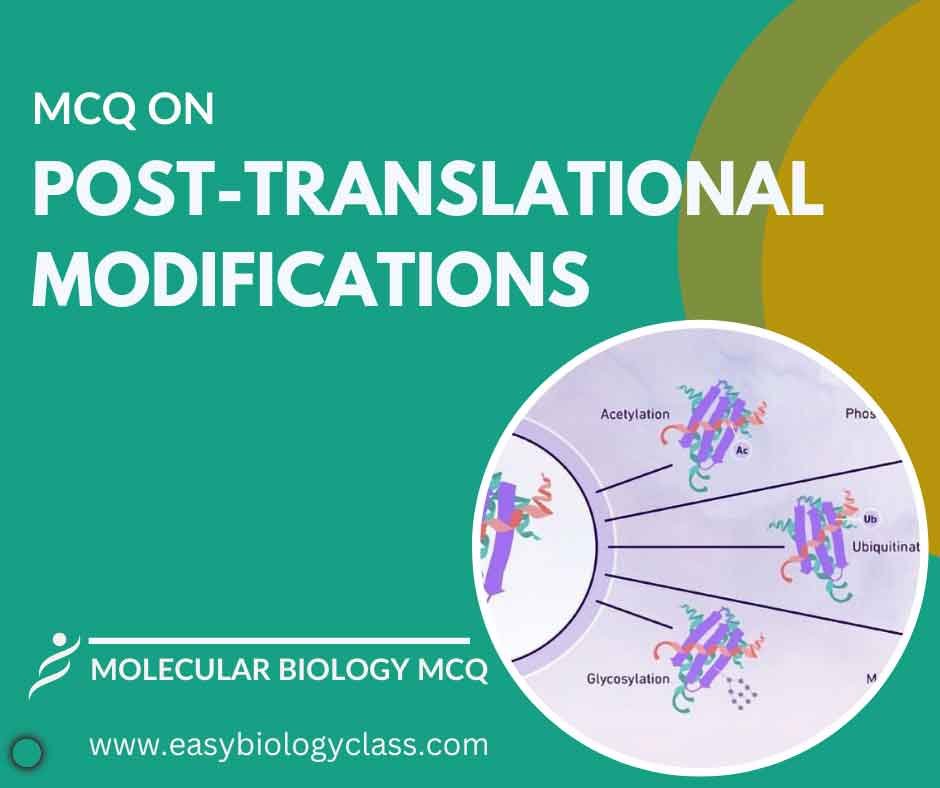
Post-translational modifications occur after protein synthesis. They include phosphorylation, glycosylation, and acetylation, altering protein structure and function. These modifications regulate protein activity, localization, and stability, crucial for cellular signaling, metabolism, and gene expression regulation in living organisms. This is an MCQ on Post Translational Modification in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes. Molecular […]
Continue ReadingTag Archives: Protein Synthesis
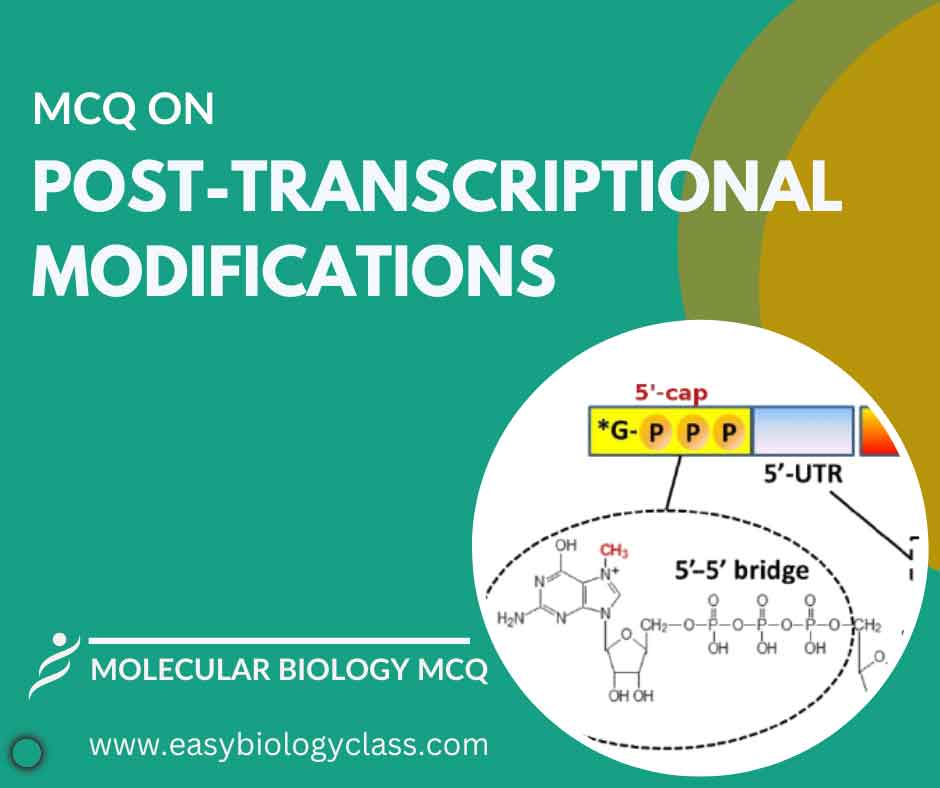
MCQ on Post Transcriptional Modification
Post-transcriptional modification refers to alterations made to mRNA molecules after transcription but before translation in eukaryotic cells. These modifications include 5′ capping, 3′ polyadenylation, and splicing, which enhance stability, regulate translation, and increase mRNA diversity, essential for proper gene expression. This is an MCQ on Post Transcriptional Modification with answer […]
Continue ReadingMCQ on Translation (Protein Synthesis)
Translation is the process by which cellular machinery converts the genetic information carried by mRNA into proteins. It occurs in the ribosomes and involves decoding the nucleotide sequence of mRNA into the corresponding sequence of amino acids, crucial for protein synthesis. This is an MCQ on Translation (Protein Synthesis) in […]
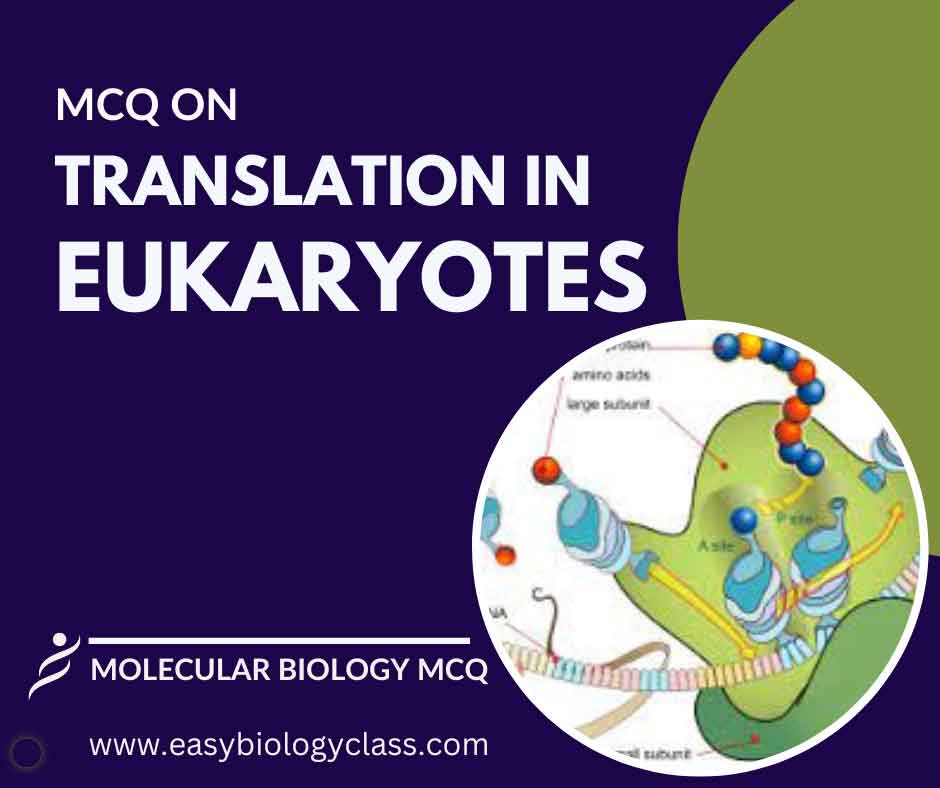
Continue ReadingMCQ on Translation in Eukaryotes
In eukaryotes, translation occurs in the cytoplasm following transcription. The mRNA, after processing, binds to ribosomes, where it is decoded by transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to assemble amino acids into a polypeptide chain. This process requires initiation, elongation, and termination factors for protein synthesis. This is an MCQ on Translation […]
Continue ReadingMCQ on Translation in Prokaryotes
In prokaryotes, translation begins while transcription is ongoing. The mRNA, produced by RNA polymerase, directly binds to ribosomes in the cytoplasm. Ribosomes then read the mRNA sequence and synthesize proteins by recruiting transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules that bring specific amino acids corresponding to the mRNA codons. This is an MCQ […]
Continue Reading