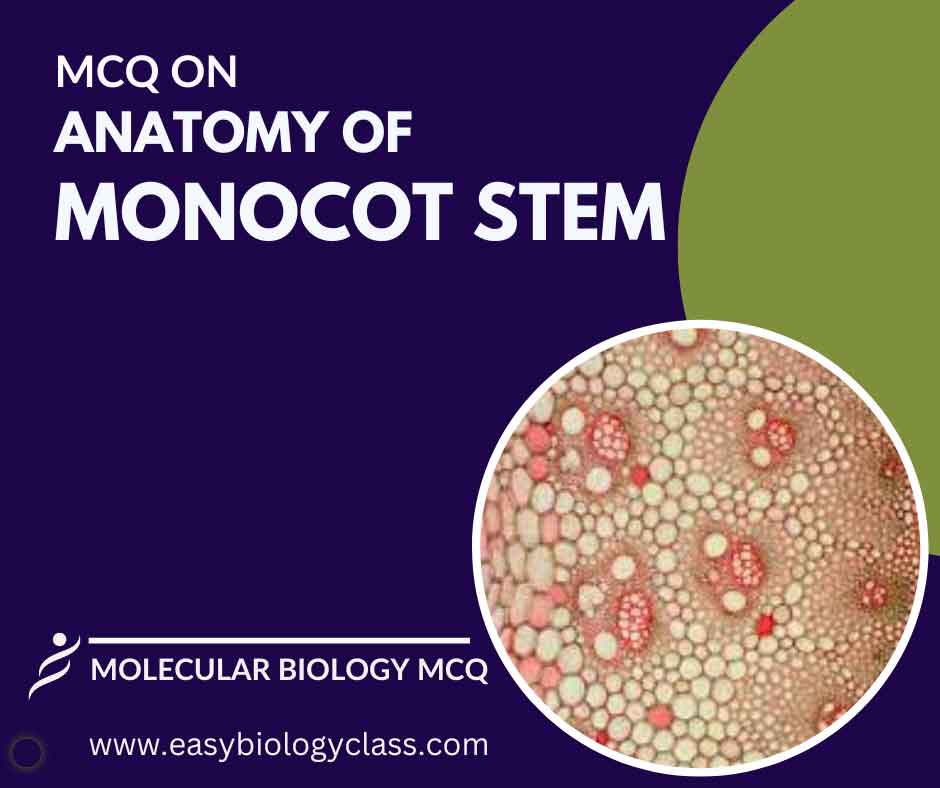
A monocot stem consists of epidermis with stomata, a scattered arrangement of vascular bundles containing xylem and phloem, and ground tissue. The stem lacks secondary growth due to the absence of a vascular cambium. A cuticle covers the epidermis. This is an MCQ on Anatomy of Monocot Stem with Answer […]
Continue ReadingTag Archives: Plant Anatomy
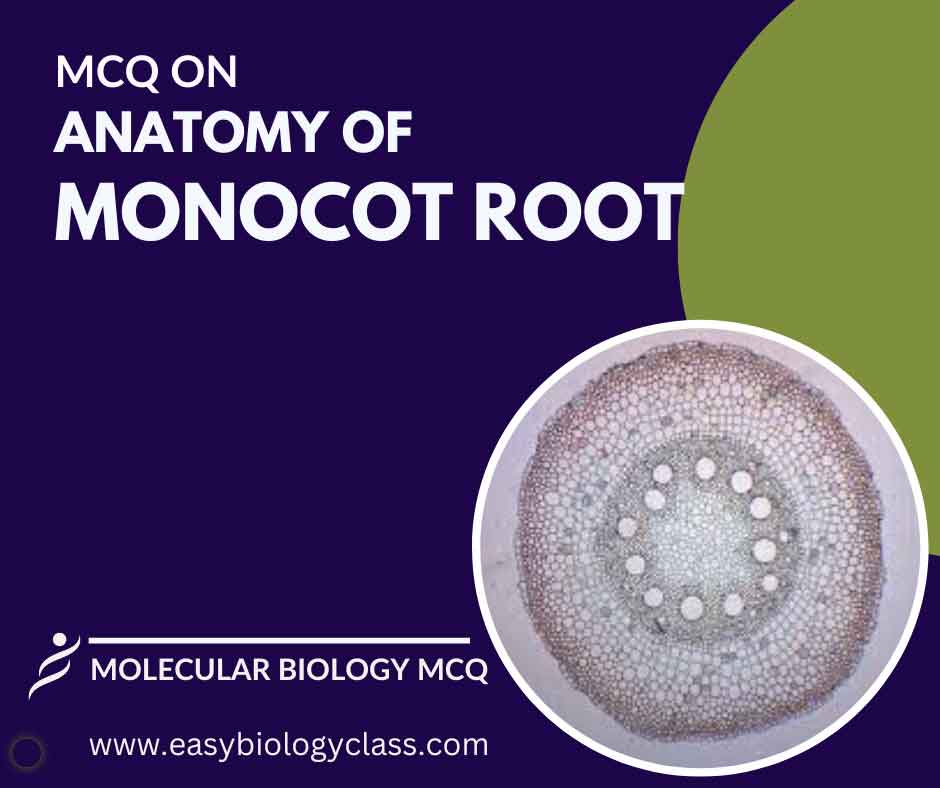
MCQ on Anatomy of Monocot Root
A monocot root comprises an epidermis with root hairs, a cortex for storage, and an endodermis with a Casparian strip. The vascular cylinder contains xylem and phloem arranged in a ring. Root cap protects the growing tip, aiding in soil penetration. This is an MCQ on Anatomy of Monocot Root. […]
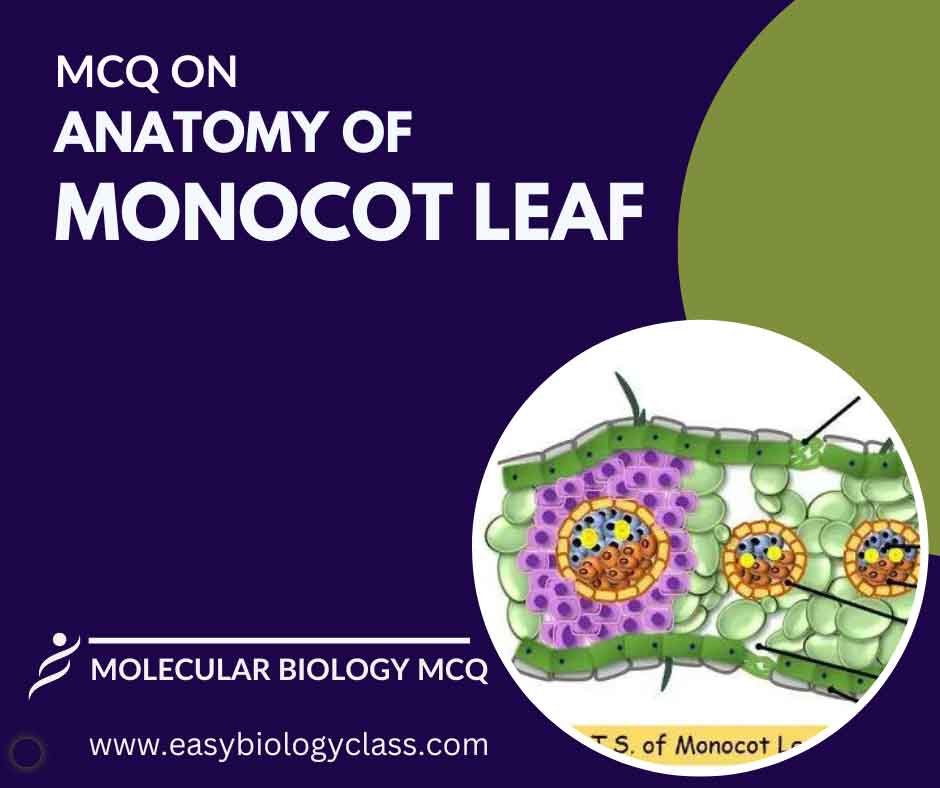
Continue ReadingMCQ on Anatomy of Monocot Leaf
A monocot leaf has a single layer of epidermis with stomata for gas exchange. Vascular bundles are scattered throughout the ground tissue, lacking a distinct arrangement. The mesophyll contains parenchyma cells for photosynthesis. A waxy cuticle covers the leaf surface. This is an MCQ on Anatomy of Monocot Leaf with […]
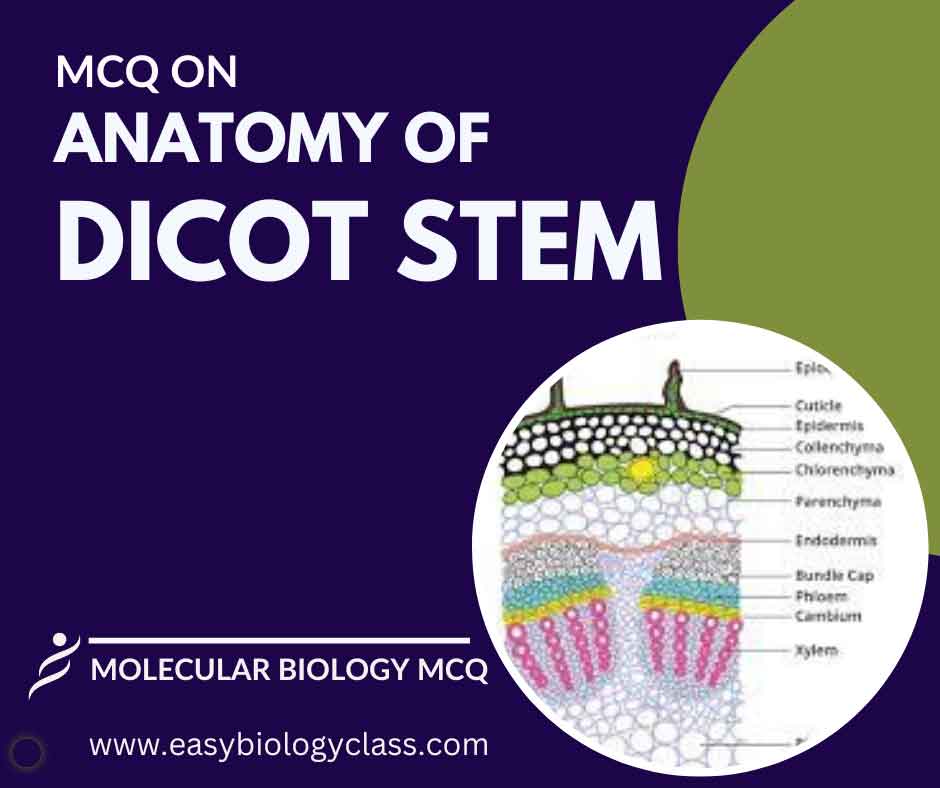
Continue ReadingMCQ on Anatomy of Dicot Stem
A dicot stem features epidermis, cortex, and pith. Vascular bundles, arranged in a ring, contain xylem for water transport and phloem for nutrient transport. The cambium layer promotes secondary growth. Stomata on the epidermis facilitate gas exchange. This is an MCQ on Anatomy of Dicot Stem with Answer Key. Botany […]
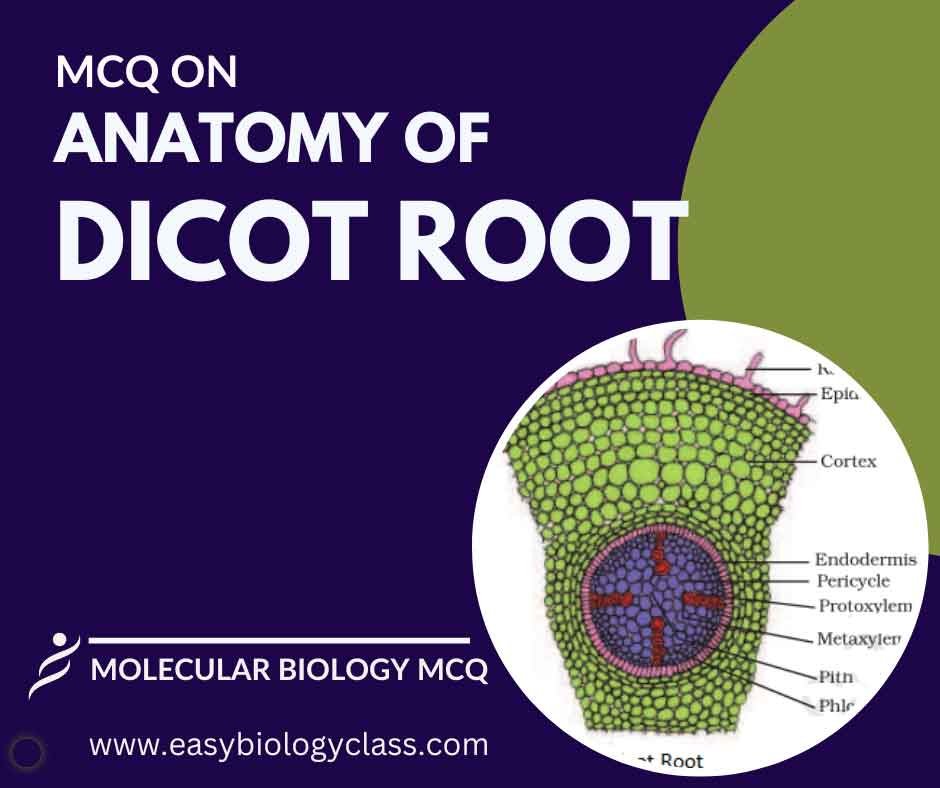
Continue ReadingMCQ on Anatomy of Dicot Root
A dicot root consists of a central vascular cylinder surrounded by cortex and endodermis. The vascular cylinder includes xylem for water transport and phloem for nutrient transport. Root hairs in the zone of maturation aid in absorption. This is an MCQ on Anatomy of Dicot Root with Answer Key. Botany […]
Continue Reading