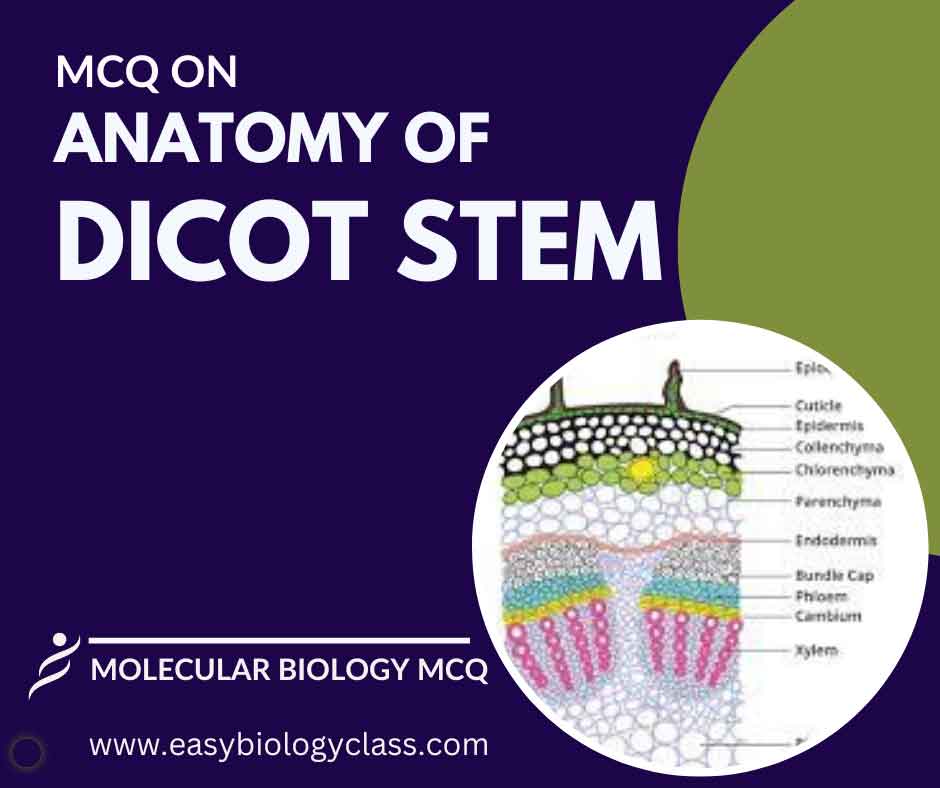
A dicot stem features epidermis, cortex, and pith. Vascular bundles, arranged in a ring, contain xylem for water transport and phloem for nutrient transport. The cambium layer promotes secondary growth. Stomata on the epidermis facilitate gas exchange. This is an MCQ on Anatomy of Dicot Stem with Answer Key. Botany […]
Continue ReadingCategory Archives: Biology MCQ
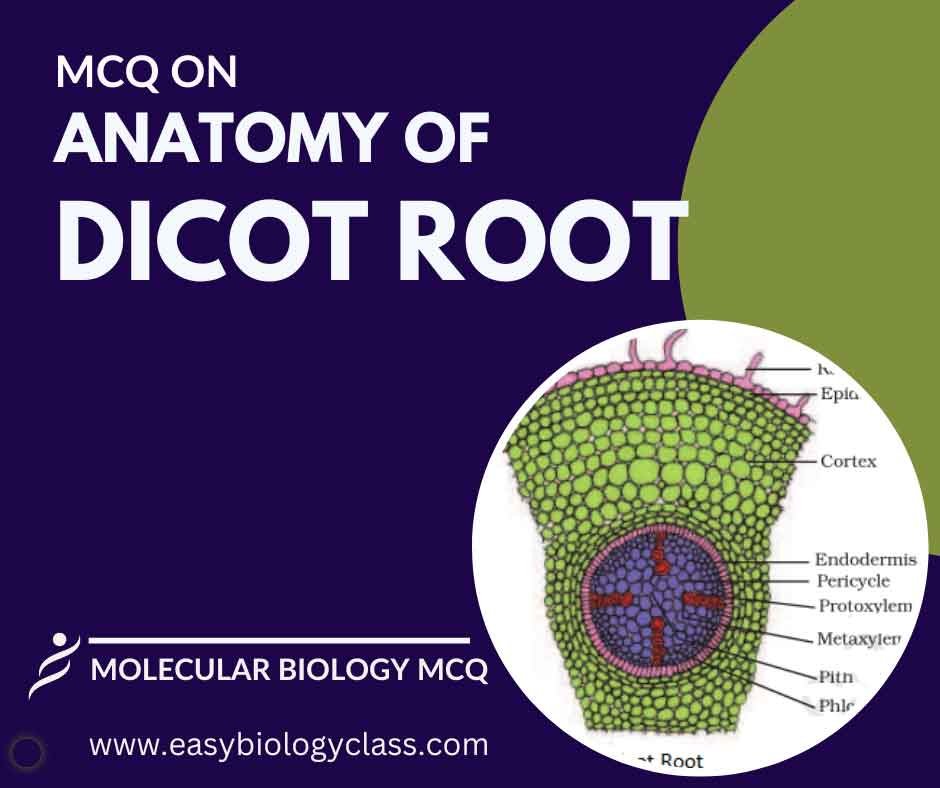
MCQ on Anatomy of Dicot Root
A dicot root consists of a central vascular cylinder surrounded by cortex and endodermis. The vascular cylinder includes xylem for water transport and phloem for nutrient transport. Root hairs in the zone of maturation aid in absorption. This is an MCQ on Anatomy of Dicot Root with Answer Key. Botany […]
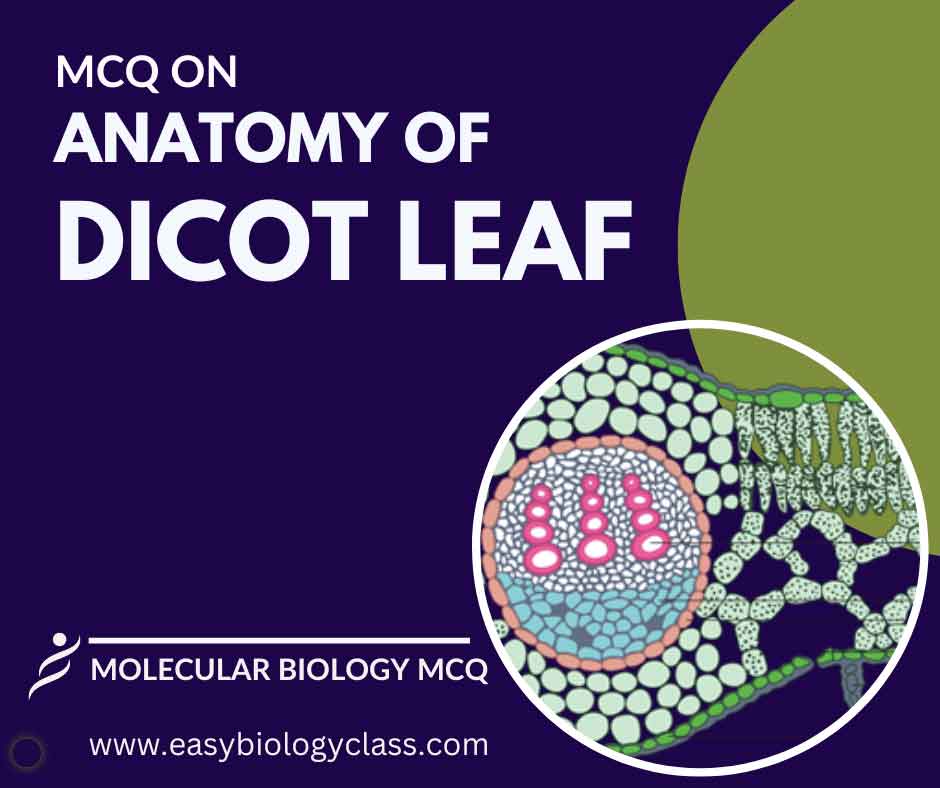
Continue ReadingMCQ on Anatomy of Dicot Leaf
A dicot leaf typically exhibits a broad, flattened shape with a reticulate venation pattern. Its structure includes an epidermis, mesophyll with palisade and spongy layers, vascular bundles arranged in a ring, and stomata for gas exchange on the lower epidermis. This is an MCQ on Anatomy of Dicot Leaf. Botany […]
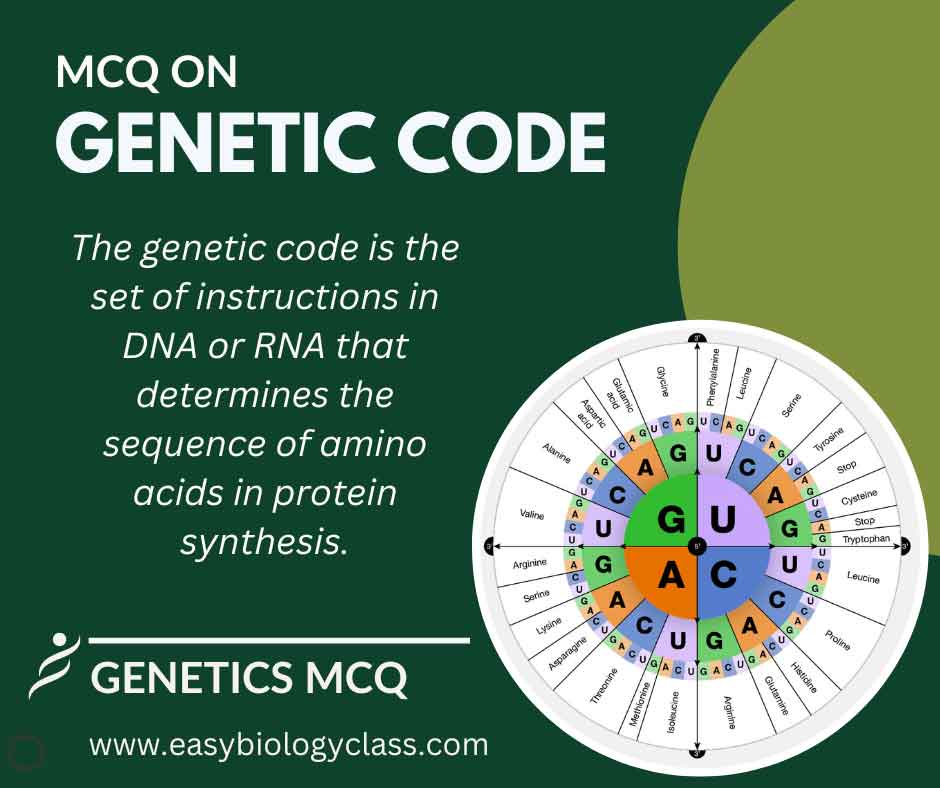
Continue ReadingMCQ on Genetic Code
Genetic code refers to the set of rules that govern the translation of genetic information carried by DNA or RNA into functional proteins. It involves the sequence of nucleotide triplets (codons), each specifying a particular amino acid or signaling the termination of protein synthesis. This is an MCQ on Genetic […]
Continue ReadingMCQ on Carbohydrates Structure and Functions
Carbohydrates are organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, typically in a 1:2:1 ratio. They serve as a primary source of energy for living organisms and include sugars, starches, and fibers found in foods like fruits, grains, and vegetables. This is an MCQ on Carbohydrates Structure and Functions. | […]
Continue Reading