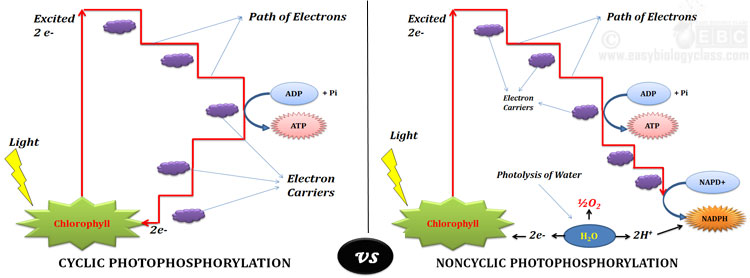
Cyclic Photophosphorylation vs Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation
Difference between Cyclic and Non Cyclic Photophosphorylation: The process of photosynthesis is completed in two main steps – Light reaction and Dark reaction. The Light reaction is the light-dependent reaction where the assimilatory powers (ATP and reduced coenzymes) are generated in the grana of chloroplasts. During the light reaction, photolysis of water and evolution of oxygen take place. In the dark reaction (light independent reaction), the assimilatory powers synthesized in the light reaction are utilized to reduce the CO2 to carbohydrates.
During the light reaction, energy in the sunlight is captured by the reaction centers of photosystems (PS I and/or PS II) and they expel electrons with high energy. These electrons then pass through a series of complexes called Electron Transport System (ETS) to synthesize the assimilatory powers. During the pathway of electrons through the ETS, phosphorylation reaction occurs at specific points which results in the synthesis of energy-rich APT molecules.
Since this phosphorylation is occurring in presence of light, it is called photophosphorylation. Depending upon the path of electrons in the electron-transport-system of the primary photochemical reaction, there are two types of photophosphorylation processes. They are (1) Cyclic photophosphorylation and (2) Noncyclic photophosphorylation.
| You may also like NOTES in... | ||
|---|---|---|
| BOTANY | BIOCHEMISTRY | MOL. BIOLOGY |
| ZOOLOGY | MICROBIOLOGY | BIOSTATISTICS |
| ECOLOGY | IMMUNOLOGY | BIOTECHNOLOGY |
| GENETICS | EMBRYOLOGY | PHYSIOLOGY |
| EVOLUTION | BIOPHYSICS | BIOINFORMATICS |
The present post discusses the similarities and differences between cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation with a comparison table.

Similarities between cyclic and noncyclic phosphorylation
Ø Both cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylations are light reactions.
Ø Both are dependent on light.
Ø Both are electron transport systems.
Ø Both pathways produce assimilatory powers.
Ø In both phosphorylation and formation of ATP occurs.
Difference between Cyclic and Noncyclic Photophosphorylation
Sl. No. Cyclic Photophosphorylation* Noncyclic photophosphorylation
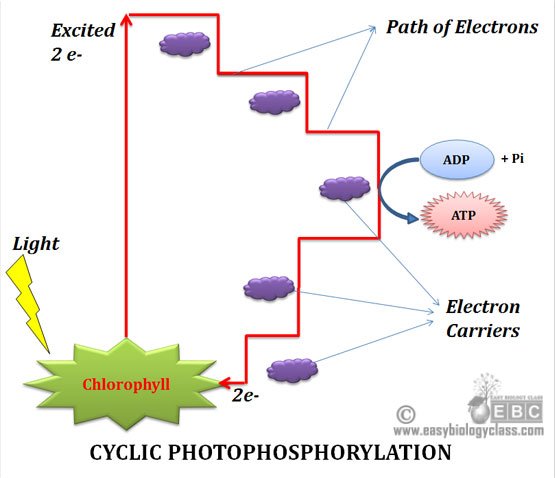
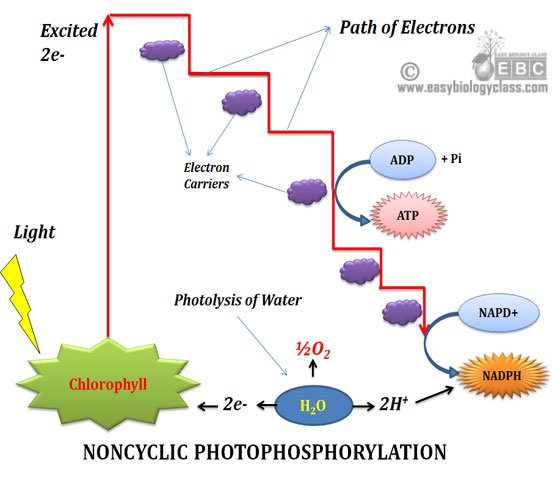
1 As the name suggests, in cyclic photophosphorylation the electrons move in a circular pattern. Electron movement is non-cyclic in noncyclic photophosphorylation.
2 Involves only Photosystem I (PS I) Involves both Photosystem I and II (PS I and PS II)
3 The electron circle is closed The electron circle is not closed
4 Electron is first expelled from the reaction center of PS I – P700 Electron is first expelled from the reaction center of PS II (P680)
5 Electron is returned back to the P700 after passing through the electron transport system (ETS) Electron is not returned to the reaction center (P680), rather it is accepted by NADP+
6 P700 is the electron donor and the final electron acceptor P680 is the first electron donor and NADP+ is the final electron acceptor
7 Photolysis of water does not occur Photolysis of water occur
8 Oxygen is not evolved Oxygen is evolved
9 Synthesize only ATP, no reduced coenzymes are synthesized Synthesize both ATP and reduced coenzymes
10 Cyclic photophosphorylation usually occurs at low light intensity Non-cyclic photophosphorylation is favoured by high light intensity
11 During anaerobic condition, the cyclic photophosphorylation predominates During aerobic condition, the non-cyclic photophosphorylation is predominates
12 Occurs when the concentration of CO2 is less in the atmosphere Occurs when the concentration of CO2 is sufficient in the atmosphere
13 Predominantly occurs in isolated chloroplasts and bacterial photosynthesis Predominantly occurs in green plants
14 Insensitive to DCMU # (cannot be inhibited by DCMU) Sensitive to DCMU (can be inhibited by DCMU)
*Photophosphorylation: The addition of phosphate group in the presence of light during the light reaction of photosynthesis is called photophosphorylation. Photophosphorylation results in the formation of ATP during light reaction.
# DCMU: It is an inhibitor of photosynthesis commonly known by the trade name Diuron. Chemically DCMU is 3-3,4-dichlorophenyl-1,1-dimethylurea. It is commonly used as an algicide and herbicide.
Cyclic Photophosphorylation (diagram)
Noncyclic Photophosphorylation (diagram)
<< Back to Plant Physiology Notes Page
You might also like…
@. Difference between Photorespiration and Respiration